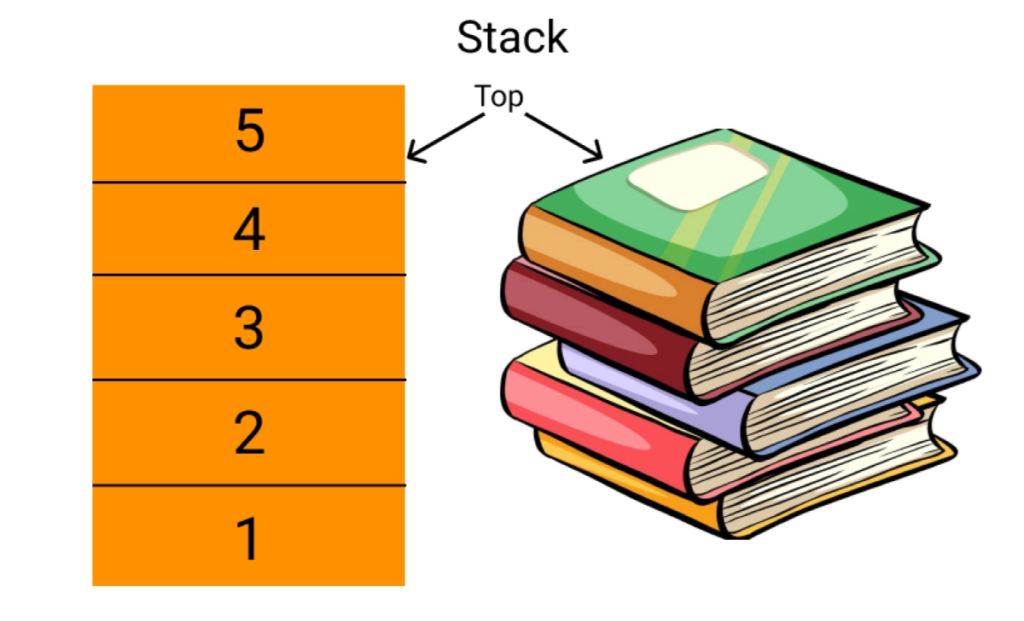
1. STACK
Definition
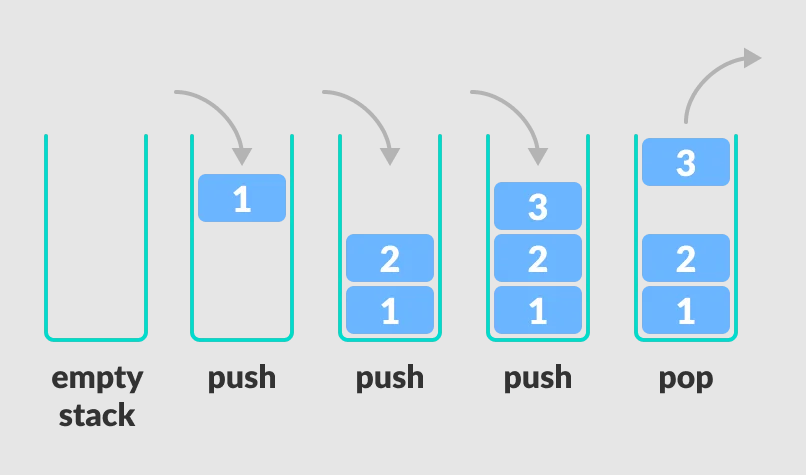
- A stack is a linear data structure that follows the Last-In-First-Out (LIFO) principle.
- Elements are inserted (PUSH) and deleted (POP) from only one end, called the TOP.
Key Operations
| Operation | Description |
|---|
| PUSH | Adds an element to the top of the stack. |
| POP | Removes the topmost element from the stack. |
| PEEK | Returns the top element without removing it. |
| isEmpty() | Checks if the stack is empty. |
| isFull() | Checks if the stack is full (for fixed-size stacks). |
Stack Terminologies
- Overflow: Occurs when trying to PUSH into a full stack.
- Underflow: Occurs when trying to POP from an empty stack.
Applications of Stack
- Function call management (Call Stack)
- Undo/Redo operations (e.g., in text editors)
- Expression evaluation (Postfix, Prefix)
- Backtracking algorithms
2. IMPLEMENTING STACK IN PYTHON
Using Lists (Dynamic Implementation)
stack = []
def push(item):
stack.append(item)
def pop():
if not is_empty():
return stack.pop()
else:
print("Underflow: Stack is empty!")
def peek():
if not is_empty():
return stack[-1]
else:
print("Stack is empty!")
def is_empty():
return len(stack) == 0
def display():
print(stack)
Menu-Driven Program
while True:
print("\n:: STACK OPERATIONS ::")
print("1. PUSH")
print("2. POP")
print("3. PEEK")
print("4. DISPLAY")
print("5. EXIT")
choice = int(input("Enter your choice: "))
if choice == 1:
item = input("Enter item to push: ")
push(item)
elif choice == 2:
print("Popped:", pop())
elif choice == 3:
print("Top element:", peek())
elif choice == 4:
display()
elif choice == 5:
break
else:
print("Invalid choice!")
3. QUEUE
Definition
- A Queue follows the First-In-First-Out (FIFO) principle.
- Elements are added (Enqueue) at the REAR and removed (Dequeue) from the FRONT.
Key Operations
| Operation | Description |
|---|
| Enqueue | Adds an element at the REAR. |
| Dequeue | Removes an element from the FRONT. |
| Peek | Returns the FRONT element without removal. |
| isEmpty() | Checks if the queue is empty. |
| isFull() | Checks if the queue is full (for fixed-size queues). |
Applications of Queue
- Printer Spooling
- CPU Scheduling
- Breadth-First Search (BFS)
- Keyboard Buffering
4. IMPLEMENTING QUEUE IN PYTHON
Using Lists (Dynamic Implementation)
queue = []
def enqueue(item):
queue.append(item)
def dequeue():
if not is_empty():
return queue.pop(0)
else:
print("Underflow: Queue is empty!")
def peek():
if not is_empty():
return queue[0]
else:
print("Queue is empty!")
def is_empty():
return len(queue) == 0
def display():
print(queue)
Menu-Driven Program
while True:
print("\n:: QUEUE OPERATIONS ::")
print("1. Enqueue")
print("2. Dequeue")
print("3. Peek")
print("4. Display")
print("5. Exit")
choice = int(input("Enter your choice: "))
if choice == 1:
item = input("Enter item to enqueue: ")
enqueue(item)
elif choice == 2:
print("Dequeued:", dequeue())
elif choice == 3:
print("Front element:", peek())
elif choice == 4:
display()
elif choice == 5:
break
else:
print("Invalid choice!")
5. VARIATIONS OF QUEUE
1. Circular Queue
- Solves the problem of unused space in a linear queue.
- Rear and Front are connected in a circular manner.
2. Deque (Double-Ended Queue)
- Allows insertion & deletion from both ends.
- Types:
- Input Restricted: Insertion at one end, deletion from both ends.
- Output Restricted: Deletion from one end, insertion from both ends.


